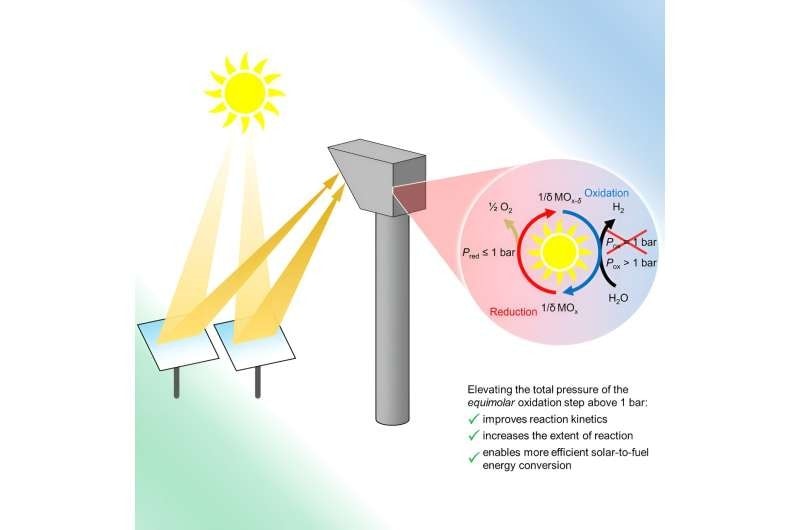
Researchers at the University of Colorado have developed a new and efficient way to produce green hydrogen or green syngas, a precursor to liquid fuels. The findings could open the door for more sustainable energy use in industries like transportation, steelmaking and ammonia production.
The new study, published Aug. 16 in the journal Joule, focuses on the production of hydrogen or syngas, a mixture of hydrogen and carbon monoxide that can be converted into fuels like gasoline, diesel and kerosene. The CU Boulder team lays the groundwork for what could be the first commercially viable method for producing this fuel, entirely using solar energy. That might help engineers to generate syngas in a more sustainable way.
The group was led by Al Weimer, professor in the Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering.
“The way I like to think about it is some day when you go to the pump you’ll have, for example, unleaded, super unleaded and ethanol options, and then an additional option being solar fuel, where the fuel is derived from sunlight, water and […]










